If you’re serious about making this business of music your full time career, then one of the first things you need to understand is the lingo of the business! Today we will discuss, in plain English, the top 7 terms you need to understand about publishing. Something important to remember about publishing is, this is how songwriters earn their living. If you are an artist who only records other peoples music, you are usually not entitled to the publishing income. However, if you are an artist who rights some or all of your own material, or a writer/ composer (beat-maker for the rap producers), this is where ALL of your money is coming from! So without any more chatter, here is:
7 Words Every Artist NEEDS To Know: Publishing
- Copyright– Copyrights are the rights given to you under US law that states, once you create an original work (known as Intellectual Property), you are the only one who is allowed to profit from it for a specified amount of time (for most of you, that would be the rest of your life, plus 70 years). Now, by law, as soon as you put the
 song in a form that anyone else can hear it or read it, it is considered copyrighted. The question is, how do you prove you did it first? Although there are a lot of suggested ideas out there on how this can be done (ie. mail it to yourself and don’t open it, upload it to a website so the date is saved, etc…) they are ALL wrong. The ONLY way to ensure that your music is protected and will stand up in court when you sue someone for stealing your song, is to register the song with the US Library of Congress. Once submitted, your copyright is secure, and you can rest assured that your music is safe.
song in a form that anyone else can hear it or read it, it is considered copyrighted. The question is, how do you prove you did it first? Although there are a lot of suggested ideas out there on how this can be done (ie. mail it to yourself and don’t open it, upload it to a website so the date is saved, etc…) they are ALL wrong. The ONLY way to ensure that your music is protected and will stand up in court when you sue someone for stealing your song, is to register the song with the US Library of Congress. Once submitted, your copyright is secure, and you can rest assured that your music is safe. - Licensing– Allowing someone else to use your music, usually in exchange for money. The amount of money can vary greatly, and depends on a) your status as an artist or songwriter, or b) the demand for your song, or c) how the song will be used (commercials, opening credits, bg music, etc.)
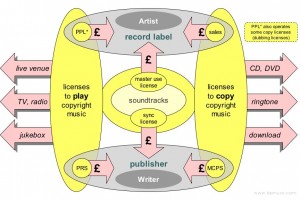
- Publishing – A) The selling and licensing of music rights within the music industry. Rights include Performance Rights (see 4. below), Mechanical Rights (see 5. below), and Sync Rights (see 6. below). B) When dealing with copyrights, and a few other aspects of the business, publishing is considered simply making a version of your music available for the public to hear. This may include CD’s, a live show, or uploading it online. So next time you file a copyright, and they ask if this work has been published, if you have released or performed the song publicly, you should check “yes”. Learn more about Publishing here.
- Performance Rights – These are the rights you will grant to people to publicly perform your music. If another band wants to cover one of your songs, when it is performed live, you are compensated.

When radio, restaurants, bars, hotels, etc… want to play your music, they also must pay for this right. However, that’s a lot of people to try to monitor yourself, so most artist use a Performance Rights Organization (or just PRO) to do this for them. The 3 PRO’s in the United States are:They will handle all licensing requests and payments on your behalf, keep a very small portion, and pay you the rest, 4 times a year.
(WARNING: The rates people pay for the Performance Rights are small, and based on some complicated math. So just because the local radio station in your town plays your songs 5 times a day, it’s not gonna be enough for you to expect a check. In reality, most artist won’t ever get a check for radio plays from a PRO, but you might get one for other
uses, like performances or getting your music played in a movie or commercial.) - Mechanical Rights – Mechanical rights are what you would offer someone who wants to record your song. Usually the label that releases this song is who will pay this. The amount owed to you is set by the US Congress, and at the time of this writing (2018) that rate is 9.1 cents, per song (long-form songs/classical music receives a different rate, contact me if you’d like to know more). Again, this can be difficult to keep track of, especially if you have many different labels who owe you money. This is where the Harry Fox Agency (now just HFA) comes in.
Like the PRO’s do for Performance Rights, if you own a publishing company (and if you write music, you should probably set one up for yourself…it’s not that hard) HFA will negotiate, collect and distribute Mechanical Licenses on your behalf. And like the PRO’s, HFA will take a small percentage in exchange. Sheet music and lyric sheets (including lyric websites), also fall under Mechanical Rights.
(WARNING: If you are an artist AND songwriter, AND you are looking to get a record deal…you will be forced most likely to accept a reduced mechanical rate because they will also be paying you a record royalty. - Sync Rights – Sync Rights are the rights you give as a songwriter to allow someone to use your music in TV, Film, and anywhere else that video and music are ‘synced’ together. If you are also an artist, and have recorded your song, you would also give a Master Use license. This would allow the tv/film producer to use the recorded version of your song that you already have (assuming you are
independent, if you’re signed, labels usually have control of the Master Use rights).There are a few ways you can get paid from a Sync license. You may work a deal where you give a royalty free license where you would get an upfront fee for your music, and the company using it can use it however much they want without having to pay you again. There are royalties paid agreements, where whomever is licensing your music would pay you each time it is played. And then there are agreements in between, (i.e. I may pay you to use your music for 3 months in an advertising campaign I’m doing. If I decide to extend that time limit, I would either give you another lump sum, or pay per use. These deals are usually worked out by whoever owns the copyright, which can get very confusing, which leads us to our last definition…..) - Publishing Company – Publishing companies were established to find songwriters like you, and have you sign over the copyrights to the music you own. “Why the hell would I do That!?!?”, you ask? Well, in exchange for giving over your copyright, the Publishing Company will take your song, and find ways for it to make money, then it will split the money earned from the song with you. Often, it’s a 50/50 split (if there’s more than 1 writer, they will all split the 50%, and the Publishing Company will keep the other 50%), but depending on you success rate, and/or how much help you need securing opportunities for your music, it is possible for you to keep the whole writers half, and also receive some of the Publishers share.
For those who have a typical publishing deal, the Publishing Company will handle much, if not all, of the paperwork and negotiations involved in all of the above mentioned licensing opportunities. I often like to think of the Publishing Company as the record label for songwriters. Of course, Publishing is the largest ($$$ and most profitable $$$) part of the music industry, so there is much, much more to know before you can call yourself a publishing expert, but these definitions will definitely put you at an advantage when the opportunity comes.






1 Comment